threshold

sidopera.png
Sydney Opera House from Dawes Point, Sydney, Australia. Greg O'Beirne, Wikimedia Commons.
Threshold sets pixels with intensities less than a given cutoff value to zero. Two variants determine how the remaining pixels are treated.
In the soft command variant (sidopera.png middle slice), threshold subtracts the cutoff intensity, c, from the image and then sets pixels with negative intensities to zero. In the middle slice, the cutoff intensity was 127, which threshold subtracted from the image, then set all pixels with intensities less than zero to zero, in essence using the cut command. The operation put the middle slice maximum intensity at 127 from an original value of 254.
In the hard variant of the command (sidopera.png right slice), threshold sets all intensities less than the cutoff to zero (127 again) and intensities equal to or greater than the cutoff to one. It converts the channel to a binary dataset with 0 or 1 values. The hard variant of threshold often prepares masks, but for use in other paint programs, it is prudent to normalize the image to a range compatible with the paint program, typically 0,255 for 8 bit programs such as Gimp.
It is possible to use threshold without parameters. This brings up the display window (see display). One may press left mouse button down in the display window and drag the pointer to the left and right to interactively set the threshold. Releasing the left mouse button sets the threshold at the last value derived from mouse movements.
Threshold may operate on multi-channel (multi-spectral) images in both soft and hard modes. In this case, the command operates independently on each channel. Threshold also works along the depth dimension, supporting multi-slice images.
Command reference
$ gmic -h threshold
threshold:
value[%],_is_soft_thresholding={ 0:No | 1:Yes }
Threshold values of selected images.
'soft' can be { 0:Hard-thresholding | 1:Soft-thresholding }.
Default value: 'is_soft=0'.
Example:
[#1] image.jpg +threshold[0] 50% +threshold[0] 50%,1
Tutorial: https://gmic.eu/tutorial/threshold
threshold:
value[%],_is_soft_thresholding={ 0:No | 1:Yes }
Threshold values of selected images.
'soft' can be { 0:Hard-thresholding | 1:Soft-thresholding }.
Default value: 'is_soft=0'.
Example:
[#1] image.jpg +threshold[0] 50% +threshold[0] 50%,1
Tutorial: https://gmic.eu/tutorial/threshold
value: Specifies the cutoff intensity below which image pixels are set to zero. May be expressed as an absolute intensity, or in percentage terms, where it expresses the fractional part of the interval, iM − im, between an image's maximum value iM and minimum value im.
___is_soft:__ an optional boolean flag. When zero, the default, -threshold produces binary images where input pixels at or exceeding the threshold value are set to logical one (True) in the output channel, and are otherwise set to zero (False). When one, -threshold produces grayscale images with new intensities reduced from the old by a difference equal to the cutoff and with negative values set to zero. In this mode, the new maximum intensity relates to the old in the following way:
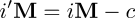
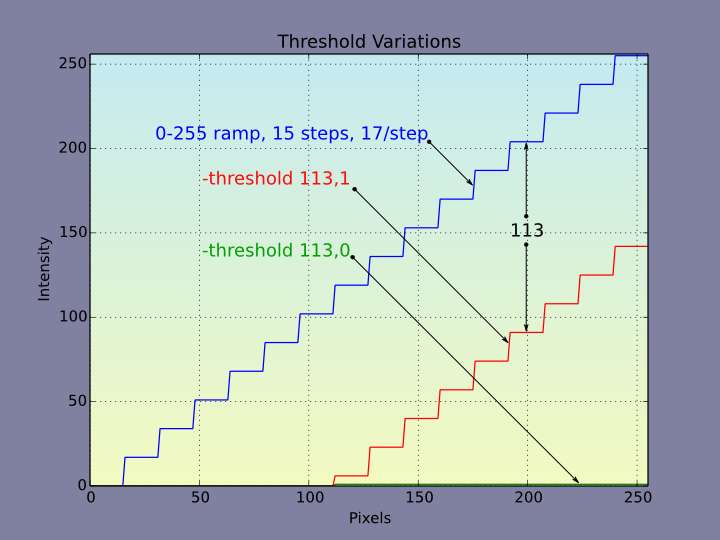
threshold_graph.jpg


 Home
Home Download
Download News
News Mastodon
Mastodon Bluesky
Bluesky X
X Summary - 17 Years
Summary - 17 Years Summary - 16 Years
Summary - 16 Years Summary - 15 Years
Summary - 15 Years Summary - 13 Years
Summary - 13 Years Summary - 11 Years
Summary - 11 Years Summary - 10 Years
Summary - 10 Years Resources
Resources Technical Reference
Technical Reference Scripting Tutorial
Scripting Tutorial Video Tutorials
Video Tutorials Wiki Pages
Wiki Pages Image Gallery
Image Gallery Color Presets
Color Presets Using libgmic
Using libgmic G'MIC Online
G'MIC Online Community
Community Discussion Forum (Pixls.us)
Discussion Forum (Pixls.us) GimpChat
GimpChat IRC
IRC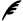 Report Issue
Report Issue